Fixxx
Moderator
- Joined
- Aug 21, 2024
- Messages
- 692
- Reaction score
- 3,465
- Points
- 93
Many people use a Firefox, but not everyone knows how to configure it properly to maintain privacy. In this article, it will be shown how to make it a bit more anonymous.
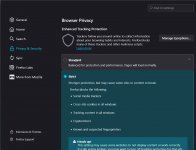
Open your browser - Settings - Privacy & Security.
In the same section, scroll down and find the Cookies and Site Data option. Select "Delete cookies and site data when Firefox is closed".
It's recommended to set the option to "Always use private browsing mode".
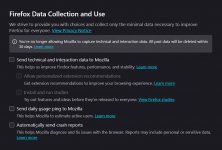
Uncheck all boxes, as telemetry sends data about your usage of Mozilla, which can be used for profiling.
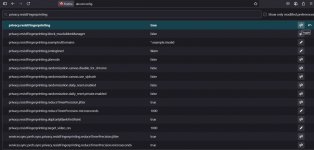
Type about:config in the address bar and click "Accept the Risk and Continue". In the search bar, type privacy.resistFingerprinting and set the value to "true". This will help reduce your digital fingerprint by spoofing browser characteristics (e.g, screen resolution, time zone).
In the settings search bar, type privacy.firstparty.isolate and set the value to "true". This will isolate cookies for the top-level domain, reducing cross-site tracking.
Enter network.cookie.cookieBehavior and set the value to "2" instead of "5".
Enter geo.enabled and set the value to "false".
In the search bar, type media.hardwaremediakeys.enabled and set the value to "false".
Enter webgl.disabled and set the value to "true".
Enter dom.webaudio.enabled and set the value to "false".
Enter beacon.enabled and set the value to "false".
Enter browser.send_pings and set the value to "false". All these settings reduce unique browser identifiers and prevent data leaks.
In the address bar, type about:addons and search for the necessary extensions:
Go to about:config, type media.peerconnection.enabled and set the value to "false". Otherwise, WebRTC may reveal your real IP address, even when using a VPN.
Step 1: Enable Strict Tracking Protection
Open your browser - Settings - Privacy & Security.
Step 2: Clear Cookies and Data
In the same section, scroll down and find the Cookies and Site Data option. Select "Delete cookies and site data when Firefox is closed".
Step 3: Browsing History
It's recommended to set the option to "Always use private browsing mode".
Step 4: Disable Telemetry and Data Collection
Uncheck all boxes, as telemetry sends data about your usage of Mozilla, which can be used for profiling.
Step 5: Change Advanced Settings
Type about:config in the address bar and click "Accept the Risk and Continue". In the search bar, type privacy.resistFingerprinting and set the value to "true". This will help reduce your digital fingerprint by spoofing browser characteristics (e.g, screen resolution, time zone).
Step 6: Isolate Cookies
In the settings search bar, type privacy.firstparty.isolate and set the value to "true". This will isolate cookies for the top-level domain, reducing cross-site tracking.
Step 7: Reject All Third-Party Cookies
Enter network.cookie.cookieBehavior and set the value to "2" instead of "5".
Step 8: Disable Geolocation Services
Enter geo.enabled and set the value to "false".
Step 9: Disable Hardware Media Keys
In the search bar, type media.hardwaremediakeys.enabled and set the value to "false".
Step 10: Disable WebGL
Enter webgl.disabled and set the value to "true".
Step 11: Disable Web Audio API
Enter dom.webaudio.enabled and set the value to "false".
Step 12: Prevent Sites from Sending Analytics Beacons
Enter beacon.enabled and set the value to "false".
Step 13: Disable Link Audit Pings
Enter browser.send_pings and set the value to "false". All these settings reduce unique browser identifiers and prevent data leaks.
Step 14: Install Privacy-Enhancing Extensions
In the address bar, type about:addons and search for the necessary extensions:
- uBlock Origin: blocks ads, trackers and malicious scripts. Set it to regularly update filter lists.
- NoScript: blocks all scripts by default; allow scripts manually for trusted sites.
- Privacy Badger: automatically blocks privacy-infringing trackers.
Step 15: Disable or Limit WebRTC
Go to about:config, type media.peerconnection.enabled and set the value to "false". Otherwise, WebRTC may reveal your real IP address, even when using a VPN.